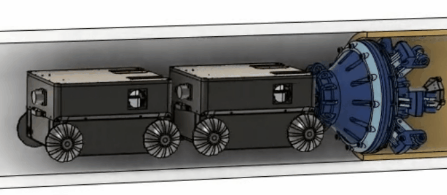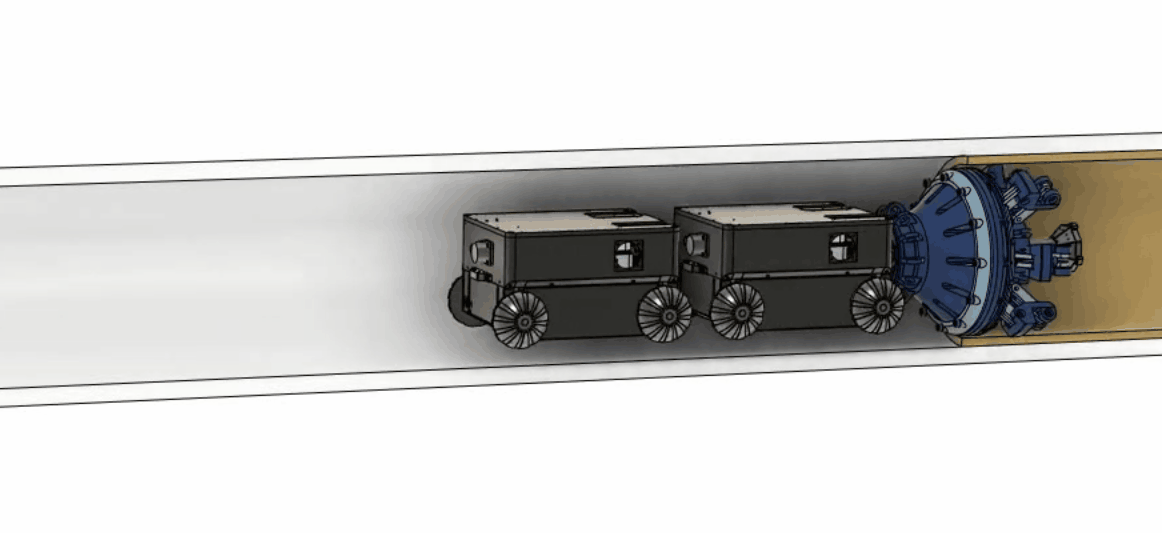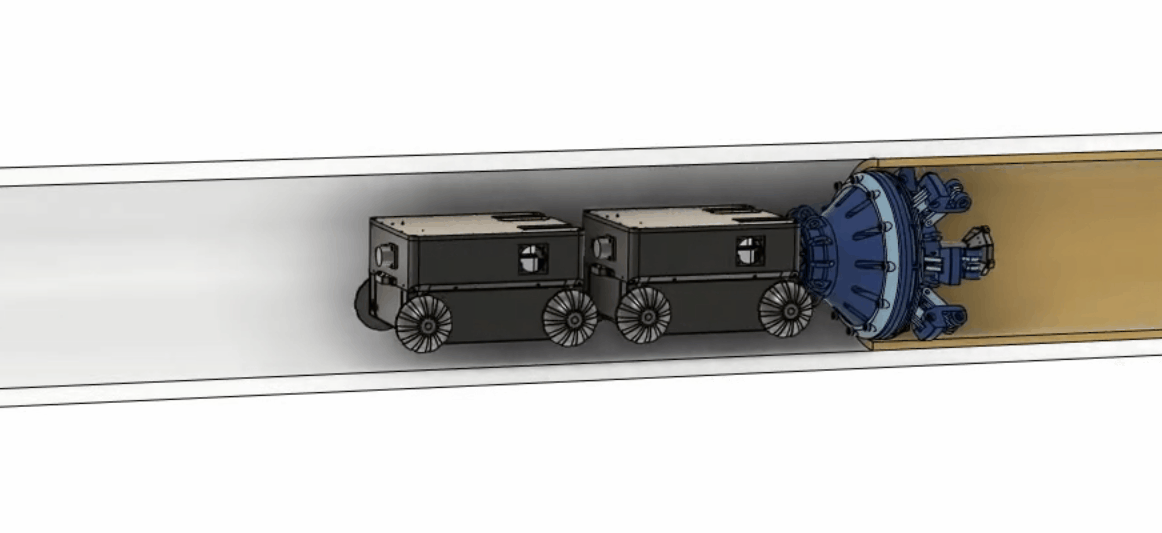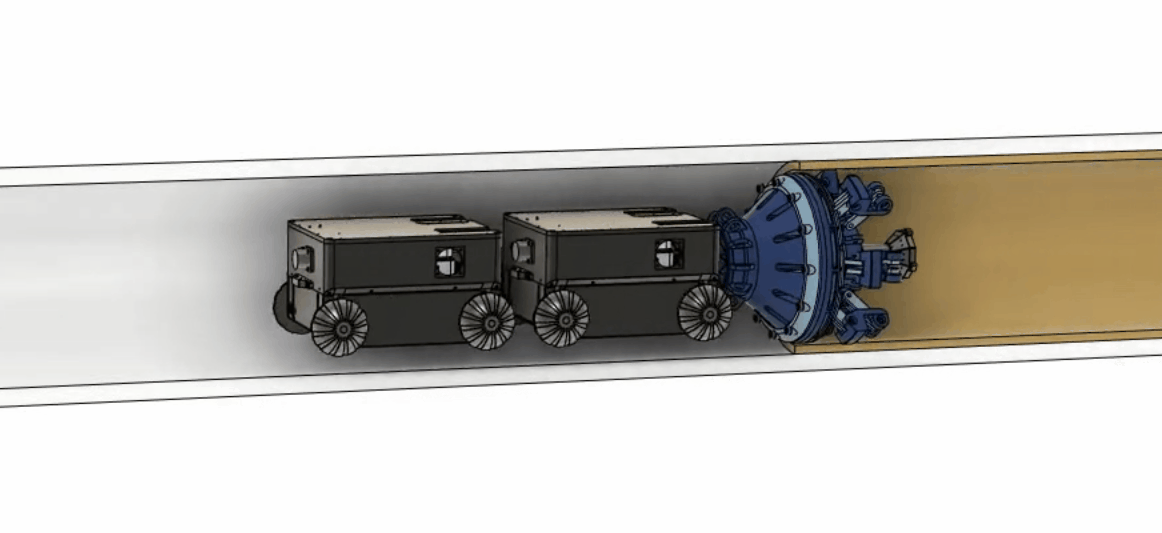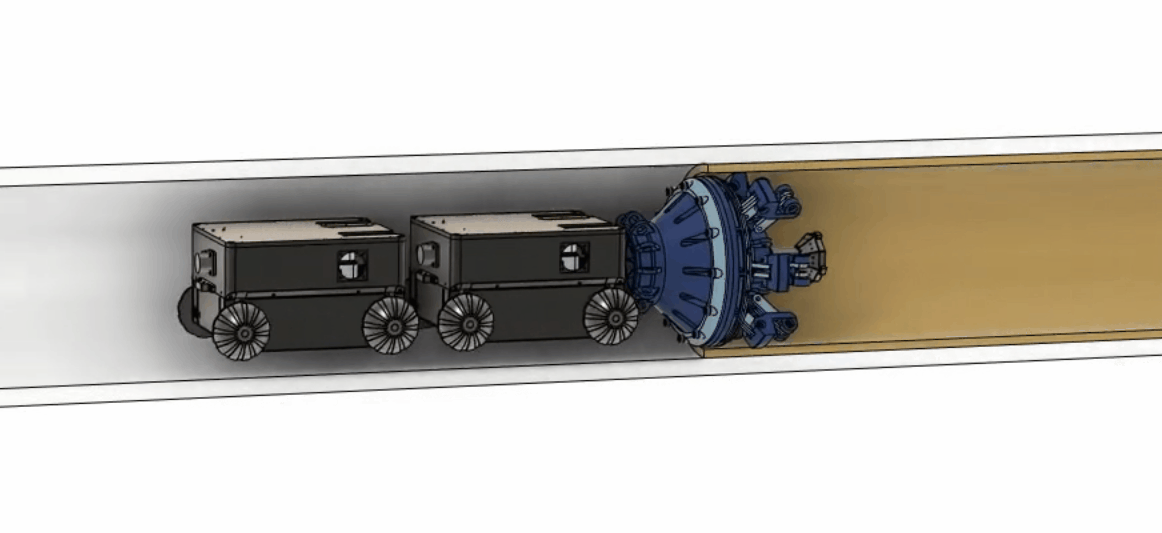
Legacy pipes make up 3% of nearly 2 million miles of utility pipes, and they are made of cast iron, wrought iron and bare steel. Some of those pipes have been underground for decades without being inspected or serviced. Leak and pipe failure occur and are proportionally high compared to most recent infrastructure. To reduce the pipe leak and make repairing the pipes safer and more cost-effective, our team is developing an in-situ repairing method with material and robotics.  Partnering up with advanced material companies and groups, we developed a robot that can carry an extrusion nozzle and liquid form of advanced materials into the pipe. Upon seeing damaged pipe walls, the robot can extrude the material at the section of the pipe that needs repair and as the material quickly hardens, constructs a structurally independent pipe within the old pipe with minimal to no disruption of gas services. The robot can perform three functions: inspection of the old pipe, construction of the new pipe, and inspection of the newly constructed pipe.
Partnering up with advanced material companies and groups, we developed a robot that can carry an extrusion nozzle and liquid form of advanced materials into the pipe. Upon seeing damaged pipe walls, the robot can extrude the material at the section of the pipe that needs repair and as the material quickly hardens, constructs a structurally independent pipe within the old pipe with minimal to no disruption of gas services. The robot can perform three functions: inspection of the old pipe, construction of the new pipe, and inspection of the newly constructed pipe.
The new pipe will be constructed with a tough and durable polymeric material. Incorporated self-healing and self-reporting functionalities coupled with the inspection components of the robotic platform can eliminate manual efforts to detect and repair damage in the new pipe material by providing real-time data and visualization. This approach, encompassing state-of-the-art robotic and smart material technology, will enable a new pipe rehabilitation solution that will lower rehabilitation and maintenance costs for over 60,000 miles of legacy pipes.